Running Apache Spark (Client mode) and Jupiter Notebooks on Kubernetes
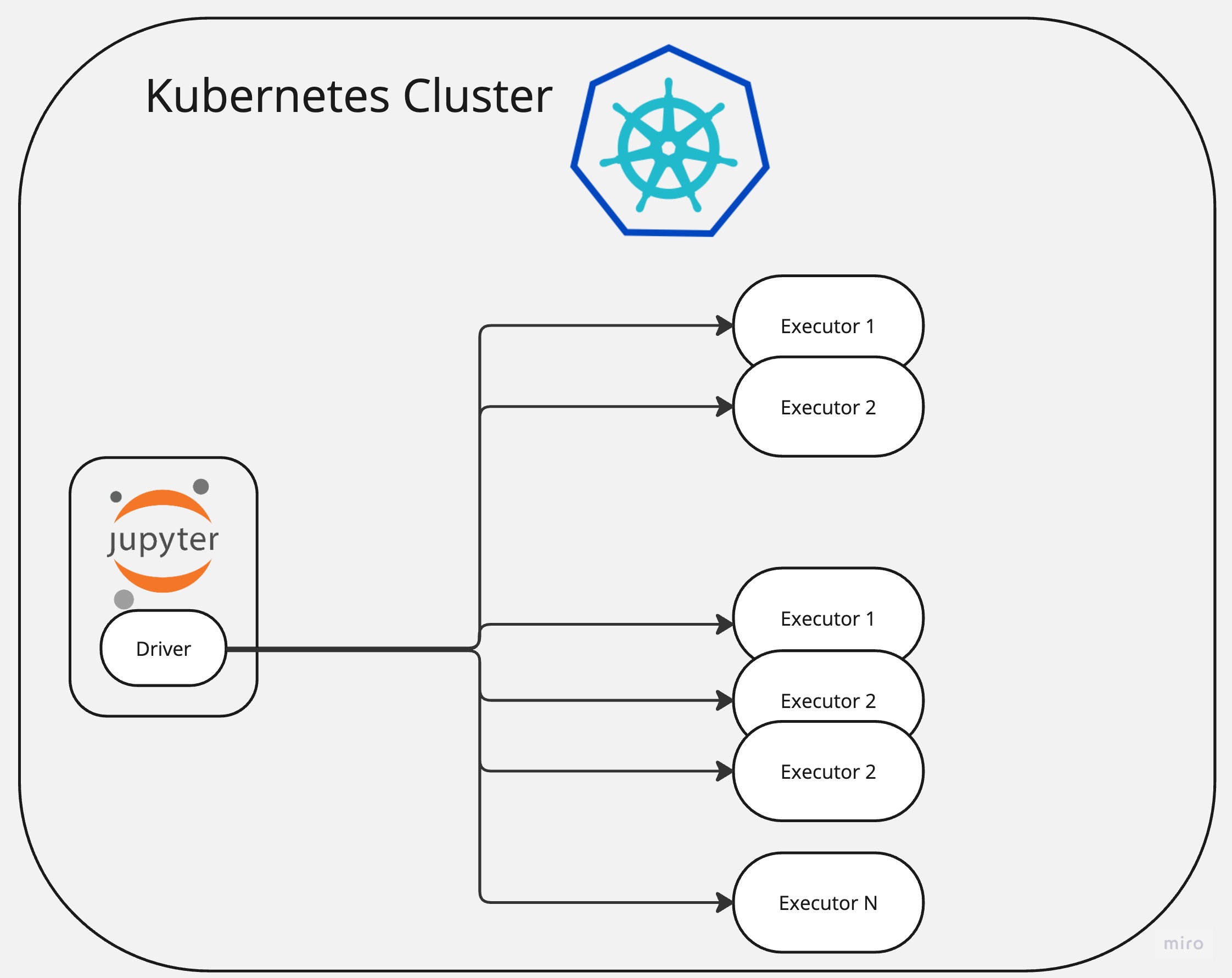
In this article I will show how to deploy Apache Spark and Jupiter Notebook to Kubernetes and interact with Spark using a Notebook.
Here Spark will be running in “Client” mode within Kubernetes. This means that a Driver will be running on a client side (and in our case within Jupiter Lab’s pod) and Workers/Executors will be dynamically allocated as per need.
Requirements
You will need running Kubernetes cluster or just use local cluster. Also, I am using a remote Linux host for docker/minikube environment and some of below commands (make) need Linux. And using Mac Book for client environment to connect to Jupiter Notebook via browser.
- docker
- minikube (optional)
Build
Jupiter Lab images provide Spark pre-packaged but it is not possible to use with latest spark images due to Python incompatibility (Jupiter Lab image uses Python 3.11 and Spark Python 3.10).
So, in order to make them aligned I am going to recompile JupiterLab image with 3.10. This feature is already provided in Jupiter Lab’s Dokerfile source codes and easy to do so.
First, lets clone Official Jupiter Lab images repo:
git clone https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks.git
cd docker-stacks
Optional, run below if you use minikube
eval $(minikube -p minikube docker-env)
Then recompile images
export DOCKER_BUILD_ARGS="--build-arg PYTHON_VERSION=3.10"
export OWNER=library
export REGISTRY=docker.io
make build-all
Verify that all images are created (some of them are not necessary for this exercise)
docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
all-spark-notebook latest e29d84984521 38 minutes ago 7.2GB
pyspark-notebook latest 31df30791633 39 minutes ago 6.36GB
datascience-notebook latest 461e586947b6 41 minutes ago 7.49GB
pytorch-notebook latest cb79cf96bbad 45 minutes ago 6.35GB
tensorflow-notebook latest 7ca4e492ea43 45 minutes ago 7.18GB
scipy-notebook latest e5aac6447efe 47 minutes ago 5.65GB
julia-notebook latest a962f004f55f 24 hours ago 2.37GB
r-notebook latest 0dc233997ffe 24 hours ago 2.78GB
quay.io/jupyter/docker-stacks-foundation latest cd9ab9cb563c 24 hours ago 397MB
minimal-notebook latest 5458db4ccc41 24 hours ago 1.52GB
base-notebook latest df66b7630f44 24 hours ago 1.03GB
Deploy Jupiter Lab
Jupiter Lab image is ready to be run but I am going to package that to a Kubernetes Deployment so I can add additional configurations and install it easily.
Below is complete YAML file. It defines Deployment for Jupiter Lab and two Services. One for web interface, so we can connect to it and one (headless) for internal pod to pod communication.
And I set newly created image as base for Jupiter Lab that will have Python 3.10. Also, applying necessary permissions to a serviceaccount called spark so it can read and launch new pods.
jupiter_spark.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: jupiter-spark
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: spark
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: spark
spec:
containers:
- name: jupiter-spark-container
image: pyspark-notebook
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: jupiter-spark-svc
namespace: default
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: spark
ports:
- port: 8888
targetPort: 8888
nodePort: 30001
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: jupiter-spark-driver-headless
spec:
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: spark
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: spark
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: pod-reader-binding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: spark
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: pod-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-edit-binding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: spark
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: edit
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Apply the yaml:
kubetctl apply -f jupiter_spark.yaml
deployment.apps/jupiter-spark created
service/jupiter-spark-svc created
service/jupiter-spark-driver-headless created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-reader created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-reader-binding created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-edit-binding created
check the installation
kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jupiter-spark-6c8756c5f9-81ei4 1/1 Running 1 (1h ago) 5m
Connect to Spark from Jupiter Notebook
All set for this step and we just need to connect to Jupiter server running on a pod. Since it’s running on a pod then we need to expose the server to outside world in order to connect to it.
Let’s run below command for it that will bind port and route outside traffic to the pod:
kubectl port-forward service/jupiter-spark-svc 7080:8888
# If you are running on a specific host and IP
# kubectl port-forward service/jupiter-spark-svc 7080:8888 --address 192.168.1.180
Now we can open Jupiter Hub on a browser:
http://localhost:7080/lab
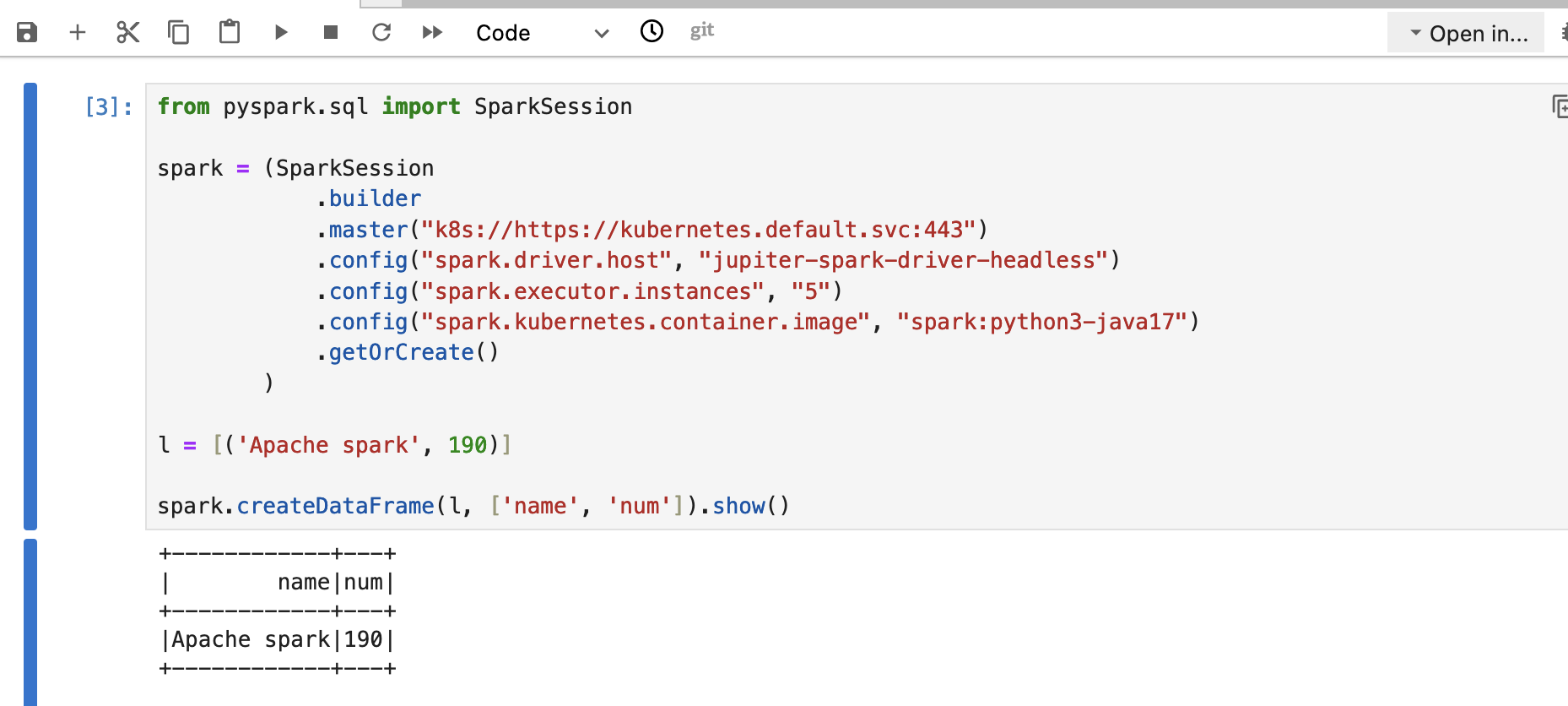
Connect and run some Spark code
Lets connect to cluster from Jupiter and run some Spark code that uses Kubernetes as a Master.
Here important part .master("k8s://https://kubernetes.default.svc:443") where we set Spark
Master to be Kubernetes so it can provision pods for executors.
Below is sample code:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = (SparkSession
.builder
.master("k8s://https://kubernetes.default.svc:443")
.config("spark.driver.host", "jupiter-spark-driver-headless")
.config("spark.executor.instances", "5")
.config("spark.kubernetes.container.image", "spark:python3-java17")
.getOrCreate()
)
l = [('Apache spark', 190)]
spark.createDataFrame(l, ['name', 'num']).show()
you should get output like below:
Stopping Session
When you finish your analysis, you will need to stop the session to remove clear up running pods. Lets check how it looks like before stopping:
kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jupiter-spark-7d45d778ff-kn28c 1/1 Running 2 (47h ago) 2d9h
pyspark-shell-0138138c1f44e7c3-exec-1 1/1 Running 0 27s
pyspark-shell-0138138c1f44e7c3-exec-2 1/1 Running 0 26s
pyspark-shell-0138138c1f44e7c3-exec-3 1/1 Running 0 26s
pyspark-shell-0138138c1f44e7c3-exec-4 1/1 Running 0 26s
pyspark-shell-0138138c1f44e7c3-exec-5 1/1 Running 0 26s
Now when you run spark.stop() in your Jupiter Lab it should stop all these executors.
Checking:
kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jupiter-spark-7d45d778ff-kn28c 1/1 Running 2 (47h ago) 2d9h
Scaling Spark cluster
Scaling cluster with Kubernetes is very easy.
Just set desired executor count in the config via “spark.executor.instances” property during session creation time:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = (SparkSession
.builder
.master("k8s://https://kubernetes.default.svc:443")
.config("spark.driver.host", "jupiter-spark-driver-headless")
.config("spark.executor.instances", "10") # <<<< Here
.config("spark.kubernetes.container.image", "spark:python3-java17")
.getOrCreate()
)
l = [('Apache spark', 190)]
spark.createDataFrame(l, ['name', 'num']).show()
Check
kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jupiter-spark-7d45d778ff-kn28c 1/1 Running 2 (47h ago) 2d9h
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-1 1/1 Running 0 58s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-10 1/1 Running 0 57s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-2 1/1 Running 0 58s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-3 1/1 Running 0 58s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-4 1/1 Running 0 58s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-5 1/1 Running 0 58s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-6 1/1 Running 0 57s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-7 1/1 Running 0 57s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-8 1/1 Running 0 57s
pyspark-shell-902b948c1f4ad29c-exec-9 1/1 Running 0 57s
Conclusion
Intention of this article was to show how it’s easy to get up and started with Spark and start running analytics on Spark using Kubernetes.
References
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/running-on-kubernetes.html
https://jupyter-docker-stacks.readthedocs.io/en/latest/using/selecting.html#jupyter-all-spark-notebook
https://github.com/jupyter/docker-stacks